Basics of Atomic Structure
Basics of Atomic Structure Notes For IIT JEE / NEET / CBSE Aspirants by GOF Academy
Atomic structure is the foundation of chemistry and is crucial for understanding how matter behaves. Atoms are the smallest units of matter and the basic building blocks of all elements. Here are the basics of atomic structure by GOF Academy coaching Centre:
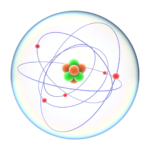
- Nucleus: At the center of an atom is the nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive charge, while neutrons are neutral (no charge). This central core is where most of the atom’s mass is concentrated.
- Electrons: Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels or electron shells. These electrons are arranged in various energy levels, with the innermost shell closest to the nucleus and subsequent shells further away. Electrons determine an atom’s chemical properties.
- Atomic Number: The atomic number (Z) of an atom is the number of protons in its nucleus. It uniquely identifies an element. All atoms of the same element have the same atomic number.
- Mass Number: The mass number of an atom is the sum of its protons and neutrons. It’s an integer value and helps define different isotopes of an element.
- Isotopes: Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons (same atomic number) but a different number of neutrons. This results in variations in mass number. Isotopes can have different physical properties but similar chemical properties.
- Electron Configuration: The electron configuration of an atom describes how electrons are distributed in its electron shells. Electrons fill the inner shells before moving to outer shells, following specific rules and orbital patterns.
- Valence Electrons: The electrons in the outermost shell of an atom are called valence electrons. These electrons are involved in chemical reactions and bonding with other atoms. The number of valence electrons largely determines an element’s chemical behavior.
- Chemical Bonds: Atoms can interact with one another by forming chemical bonds to achieve a stable electron configuration. Common types of chemical bonds include covalent bonds, where electrons are shared, and ionic bonds, where electrons are transferred between atoms.
- Molecules: When two or more atoms chemically bond together, they form molecules. Molecules can be composed of atoms of the same element (diatomic molecules like O2 and N2) or different elements (e.g., H2O, CO2).
- Atomic Mass: The atomic mass of an atom is the weighted average of the masses of its naturally occurring isotopes. It is measured in atomic mass units (amu).
- Periodic Table: The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of elements based on their atomic number. It groups elements with similar properties into columns (groups) and arranges them in order of increasing atomic number in rows (periods).
Understanding the atomic structure is fundamental in chemistry, as it helps explain how elements interact with each other to form compounds and molecules. It’s the basis for the study of chemical reactions and the behavior of matter at the atomic and molecular levels.
#atomicstructure #chemistry #neetchemistry #neetphysics #iitjee #neet #studymaterials #notes #gofacademy #gofacademydwarka #iitjeecoachingindwarka #neetcoachingindwarka